-
Reading Roadmap
- 389-P: The Role of ChREBP-ß in Exacerbating Fructose-Induced Kidney Tubule Reabsorption Issues through Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Mitochondrial Dysfunction Regulation
- Key Takeaways
- Unraveling the Role of ChREBP-ß in Kidney Health
- The Connection between Fructose, ChREBP-ß, and Kidney Disease
- Implications for Treatment and Prevention
- FAQ Section
- What is ChREBP-ß?
- How does high fructose consumption lead to kidney disease?
- What is endoplasmic reticulum stress?
- What is mitochondrial dysfunction?
- How can understanding the role of ChREBP-ß help in the treatment and prevention of kidney disease?
- Conclusion: The Crucial Role of ChREBP-ß in Kidney Health
- Further Analysis
- Key Takeaways Revisited
389-P: The Role of ChREBP-ß in Exacerbating Fructose-Induced Kidney Tubule Reabsorption Issues through Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Mitochondrial Dysfunction Regulation
[youtubomatic_search]
Key Takeaways
- ChREBP-ß plays a significant role in fructose-induced kidney tubule reabsorption issues.
- Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) stress and mitochondrial dysfunction are key factors in the development of these kidney issues.
- High fructose consumption can lead to kidney disease through the activation of ChREBP-ß.
- Understanding the role of ChREBP-ß could lead to new therapeutic strategies for kidney disease.
- Further research is needed to fully understand the complex mechanisms involved in fructose-induced kidney disease.
Unraveling the Role of ChREBP-ß in Kidney Health
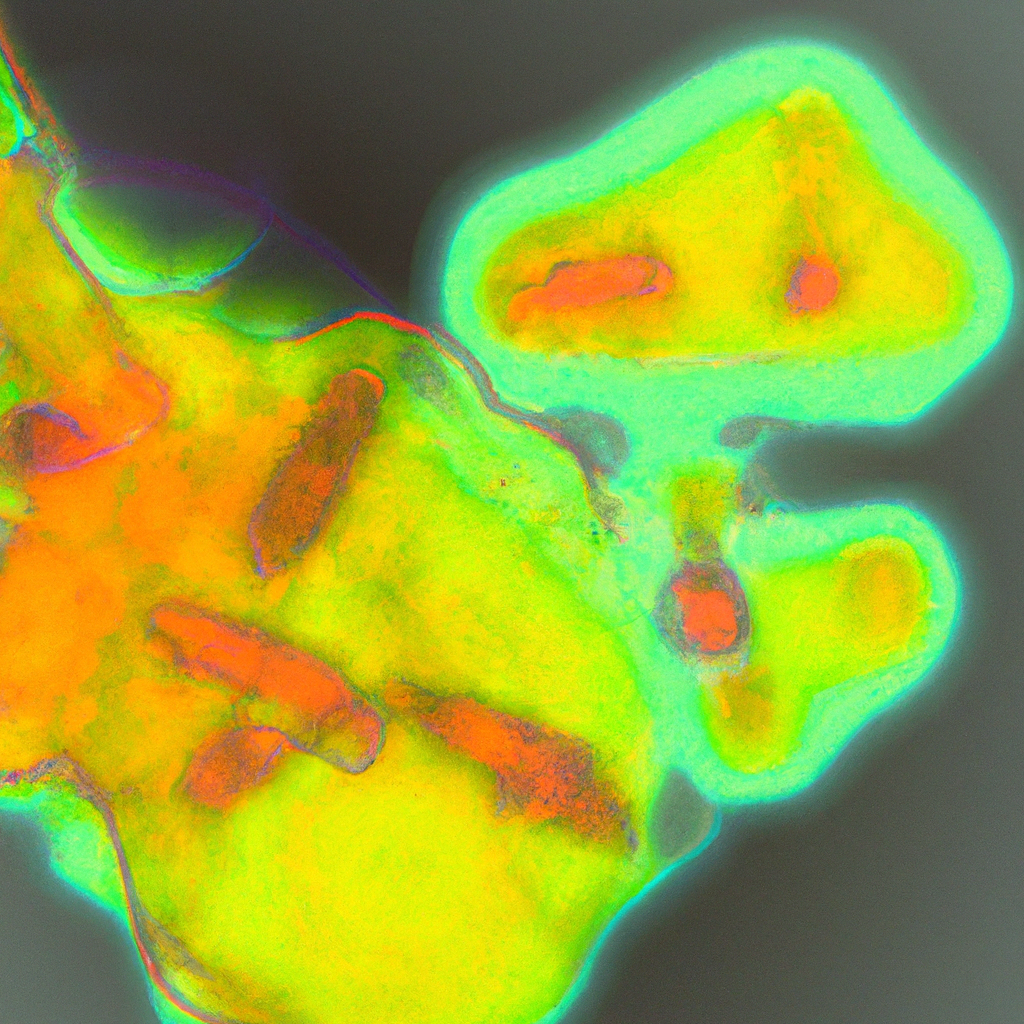
The carbohydrate-responsive element-binding protein beta (ChREBP-ß) is a transcription factor that plays a crucial role in the metabolism of glucose and lipids. Recent studies have shown that ChREBP-ß is also involved in fructose-induced kidney tubule reabsorption issues, leading to kidney disease. This article delves into the role of ChREBP-ß in exacerbating these kidney issues through the regulation of endoplasmic reticulum stress and mitochondrial dysfunction.
The Connection between Fructose, ChREBP-ß, and Kidney Disease
High fructose consumption has been linked to various health issues, including obesity, diabetes, and kidney disease. The mechanism behind this connection involves the activation of ChREBP-ß, which in turn leads to endoplasmic reticulum stress and mitochondrial dysfunction. These two factors are known to play a significant role in the development of kidney disease.
Endoplasmic reticulum stress occurs when there is an imbalance in the protein folding capacity of the ER, leading to the accumulation of misfolded proteins. This can trigger a series of events that result in cell death, inflammation, and fibrosis, all of which contribute to kidney disease. On the other hand, mitochondrial dysfunction can lead to increased production of reactive oxygen species, which can cause cellular damage and contribute to the progression of kidney disease.
Implications for Treatment and Prevention
Understanding the role of ChREBP-ß in fructose-induced kidney disease could open up new avenues for treatment and prevention. For instance, strategies that aim to reduce ChREBP-ß activity could potentially alleviate ER stress and mitochondrial dysfunction, thereby preventing the progression of kidney disease. However, further research is needed to fully understand the complex mechanisms involved and to develop effective therapeutic strategies.
FAQ Section
What is ChREBP-ß?
ChREBP-ß is a transcription factor that plays a crucial role in the metabolism of glucose and lipids. It is also involved in fructose-induced kidney tubule reabsorption issues.
How does high fructose consumption lead to kidney disease?
High fructose consumption can lead to kidney disease through the activation of ChREBP-ß, which in turn leads to endoplasmic reticulum stress and mitochondrial dysfunction.
What is endoplasmic reticulum stress?
Endoplasmic reticulum stress occurs when there is an imbalance in the protein folding capacity of the ER, leading to the accumulation of misfolded proteins. This can trigger a series of events that result in cell death, inflammation, and fibrosis, all of which contribute to kidney disease.
What is mitochondrial dysfunction?
Mitochondrial dysfunction can lead to increased production of reactive oxygen species, which can cause cellular damage and contribute to the progression of kidney disease.
How can understanding the role of ChREBP-ß help in the treatment and prevention of kidney disease?
Understanding the role of ChREBP-ß in fructose-induced kidney disease could open up new avenues for treatment and prevention. Strategies that aim to reduce ChREBP-ß activity could potentially alleviate ER stress and mitochondrial dysfunction, thereby preventing the progression of kidney disease.
Conclusion: The Crucial Role of ChREBP-ß in Kidney Health
In conclusion, ChREBP-ß plays a significant role in fructose-induced kidney tubule reabsorption issues through the regulation of endoplasmic reticulum stress and mitochondrial dysfunction. High fructose consumption can lead to kidney disease through the activation of ChREBP-ß. Understanding this mechanism could lead to new therapeutic strategies for kidney disease. However, further research is needed to fully understand the complex mechanisms involved.
[youtubomatic_search]
Further Analysis
While the role of ChREBP-ß in fructose-induced kidney disease is becoming clearer, many questions remain. For instance, what are the specific mechanisms through which ChREBP-ß regulates ER stress and mitochondrial dysfunction? How can we effectively reduce ChREBP-ß activity to prevent kidney disease? These are some of the questions that future research needs to address.
Key Takeaways Revisited
- ChREBP-ß plays a significant role in fructose-induced kidney tubule reabsorption issues.
- Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) stress and mitochondrial dysfunction are key factors in the development of these kidney issues.
- High fructose consumption can lead to kidney disease through the activation of ChREBP-ß.
- Understanding the role of ChREBP-ß could lead to new therapeutic strategies for kidney disease.
- Further research is needed to fully understand the complex mechanisms involved in fructose-induced kidney disease.

Leave a Reply