-
Reading Roadmap
- Müller Cells with Exosomal lncRNA OGRU Influence Microglia Polarization in Diabetic Retinopathy by Acting as miRNA Sponges
- Key Takeaways
- Introduction: The Role of Müller Cells and Exosomal lncRNA OGRU in Diabetic Retinopathy
- Müller Cells and Microglia Polarization
- Exosomal lncRNA OGRU as a miRNA Sponge
- Implications for Diabetic Retinopathy Treatment
- FAQ Section
- What are Müller cells?
- What is microglia polarization?
- What is exosomal lncRNA OGRU?
- How does exosomal lncRNA OGRU contribute to diabetic retinopathy?
- How could this research impact the treatment of diabetic retinopathy?
- Conclusion: The Potential of Müller Cells and Exosomal lncRNA OGRU as Therapeutic Targets
- Further Analysis
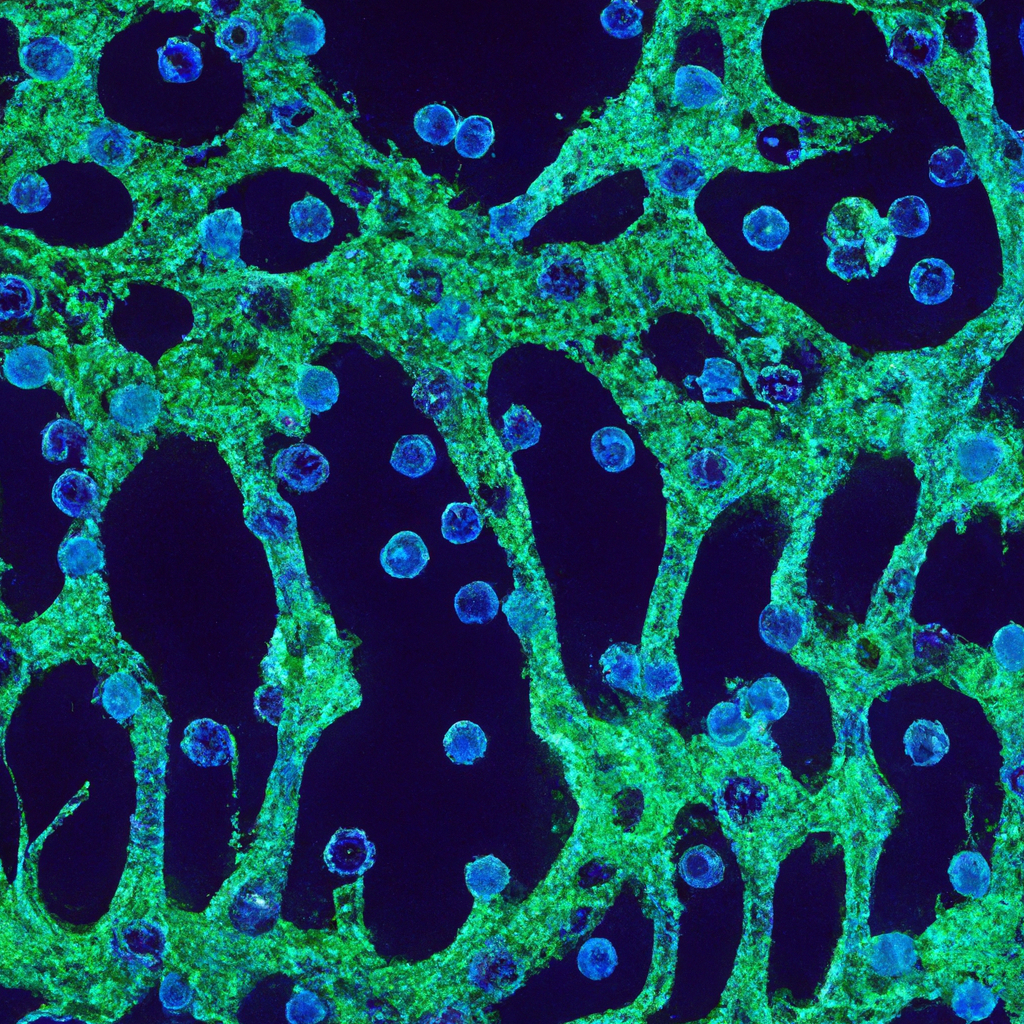
Müller Cells with Exosomal lncRNA OGRU Influence Microglia Polarization in Diabetic Retinopathy by Acting as miRNA Sponges
[youtubomatic_search]
Key Takeaways
- Müller cells with exosomal lncRNA OGRU play a significant role in the progression of diabetic retinopathy.
- These cells influence microglia polarization, a process that contributes to inflammation and neurodegeneration in the retina.
- Exosomal lncRNA OGRU acts as a miRNA sponge, absorbing miRNAs and preventing them from performing their usual functions.
- This process can lead to the exacerbation of diabetic retinopathy, a common complication of diabetes that can lead to vision loss.
- Understanding the role of Müller cells and exosomal lncRNA OGRU in diabetic retinopathy could lead to new therapeutic strategies for this condition.
Introduction: The Role of Müller Cells and Exosomal lncRNA OGRU in Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy is a common complication of diabetes that can lead to vision loss if not properly managed. Recent research has shed light on the role of Müller cells with exosomal lncRNA OGRU in the progression of this condition. These cells influence microglia polarization, a process that contributes to inflammation and neurodegeneration in the retina. Furthermore, exosomal lncRNA OGRU acts as a miRNA sponge, absorbing miRNAs and preventing them from performing their usual functions. This process can exacerbate diabetic retinopathy, highlighting the need for a deeper understanding of these mechanisms and their potential as therapeutic targets.
Müller Cells and Microglia Polarization
Müller cells are a type of glial cell found in the retina. They play a crucial role in maintaining the health and function of retinal neurons. However, in conditions like diabetic retinopathy, Müller cells can become reactive, leading to inflammation and neurodegeneration.
One of the ways Müller cells contribute to this process is through the polarization of microglia, the resident immune cells of the retina. In response to injury or disease, microglia can adopt a pro-inflammatory (M1) or anti-inflammatory (M2) phenotype. Müller cells with exosomal lncRNA OGRU can influence this polarization, promoting a pro-inflammatory state that exacerbates diabetic retinopathy.
Exosomal lncRNA OGRU as a miRNA Sponge
Exosomal lncRNA OGRU is a type of long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) that is packaged into exosomes and released by Müller cells. This lncRNA has been found to act as a miRNA sponge, absorbing miRNAs and preventing them from performing their usual functions.
miRNAs are small non-coding RNAs that play a crucial role in regulating gene expression. By sponging up these miRNAs, exosomal lncRNA OGRU can disrupt normal gene regulation, leading to increased inflammation and neurodegeneration in the retina.
Implications for Diabetic Retinopathy Treatment
The role of Müller cells with exosomal lncRNA OGRU in diabetic retinopathy highlights a potential new avenue for treatment. By targeting these cells and their exosomal lncRNA, it may be possible to reduce inflammation and neurodegeneration in the retina, slowing the progression of diabetic retinopathy.
FAQ Section
What are Müller cells?
Müller cells are a type of glial cell found in the retina. They play a crucial role in maintaining the health and function of retinal neurons.
What is microglia polarization?
Microglia polarization refers to the process by which microglia, the resident immune cells of the retina, adopt a pro-inflammatory (M1) or anti-inflammatory (M2) phenotype in response to injury or disease.
What is exosomal lncRNA OGRU?
Exosomal lncRNA OGRU is a type of long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) that is packaged into exosomes and released by Müller cells. This lncRNA can act as a miRNA sponge, absorbing miRNAs and disrupting normal gene regulation.
How does exosomal lncRNA OGRU contribute to diabetic retinopathy?
By sponging up miRNAs, exosomal lncRNA OGRU can disrupt normal gene regulation, leading to increased inflammation and neurodegeneration in the retina. This process can exacerbate diabetic retinopathy.
How could this research impact the treatment of diabetic retinopathy?
Understanding the role of Müller cells and exosomal lncRNA OGRU in diabetic retinopathy could lead to new therapeutic strategies. By targeting these cells and their exosomal lncRNA, it may be possible to reduce inflammation and neurodegeneration in the retina, slowing the progression of diabetic retinopathy.
Conclusion: The Potential of Müller Cells and Exosomal lncRNA OGRU as Therapeutic Targets
The role of Müller cells with exosomal lncRNA OGRU in diabetic retinopathy is a promising area of research. These cells influence microglia polarization, contributing to inflammation and neurodegeneration in the retina. Furthermore, exosomal lncRNA OGRU acts as a miRNA sponge, disrupting normal gene regulation and exacerbating diabetic retinopathy. Understanding these mechanisms could lead to new therapeutic strategies for this common and potentially devastating complication of diabetes.
[youtubomatic_search]
Further Analysis
While this research provides valuable insights into the pathogenesis of diabetic retinopathy, further studies are needed to fully understand the role of Müller cells and exosomal lncRNA OGRU in this condition. Future research should also explore the potential of these cells and their exosomal lncRNA as therapeutic targets, with the aim of developing more effective treatments for diabetic retinopathy.

Leave a Reply