-
Reading Roadmap
- Deep Learning Assisted Quantification of Islets for Type 1 Diabetes: A 77-PUB Study
- Key Takeaways
- Introduction: The Intersection of Deep Learning and Diabetes Research
- Deep Learning and Islet Quantification
- The 77-PUB Study: A Game-Changer
- Challenges and Future Directions
- FAQ Section
- What is deep learning?
- What are islets?
- How can deep learning help in islet quantification?
- What is the 77-PUB study?
- What are the challenges in implementing deep learning in medical research?
- Conclusion: The Future of Deep Learning in Diabetes Research
- Further Analysis
Deep Learning Assisted Quantification of Islets for Type 1 Diabetes: A 77-PUB Study
[youtubomatic_search]
Key Takeaways
- Deep learning algorithms can significantly improve the quantification of islets in Type 1 Diabetes research.
- The 77-PUB study demonstrates the potential of deep learning in medical research and diagnosis.
- Deep learning can help in the early detection and treatment of Type 1 Diabetes.
- Challenges remain in the implementation of deep learning in medical research, including data privacy and algorithm transparency.
- Further research and collaboration between medical and tech industries are needed to fully realize the potential of deep learning in healthcare.
Introduction: The Intersection of Deep Learning and Diabetes Research
Deep learning, a subset of artificial intelligence, has been making waves in various sectors, including healthcare. Its potential to revolutionize medical research and diagnosis is immense, particularly in the field of Type 1 Diabetes. This article delves into the 77-PUB study, which explores the use of deep learning in the quantification of islets, a crucial aspect of Type 1 Diabetes research.
Deep Learning and Islet Quantification
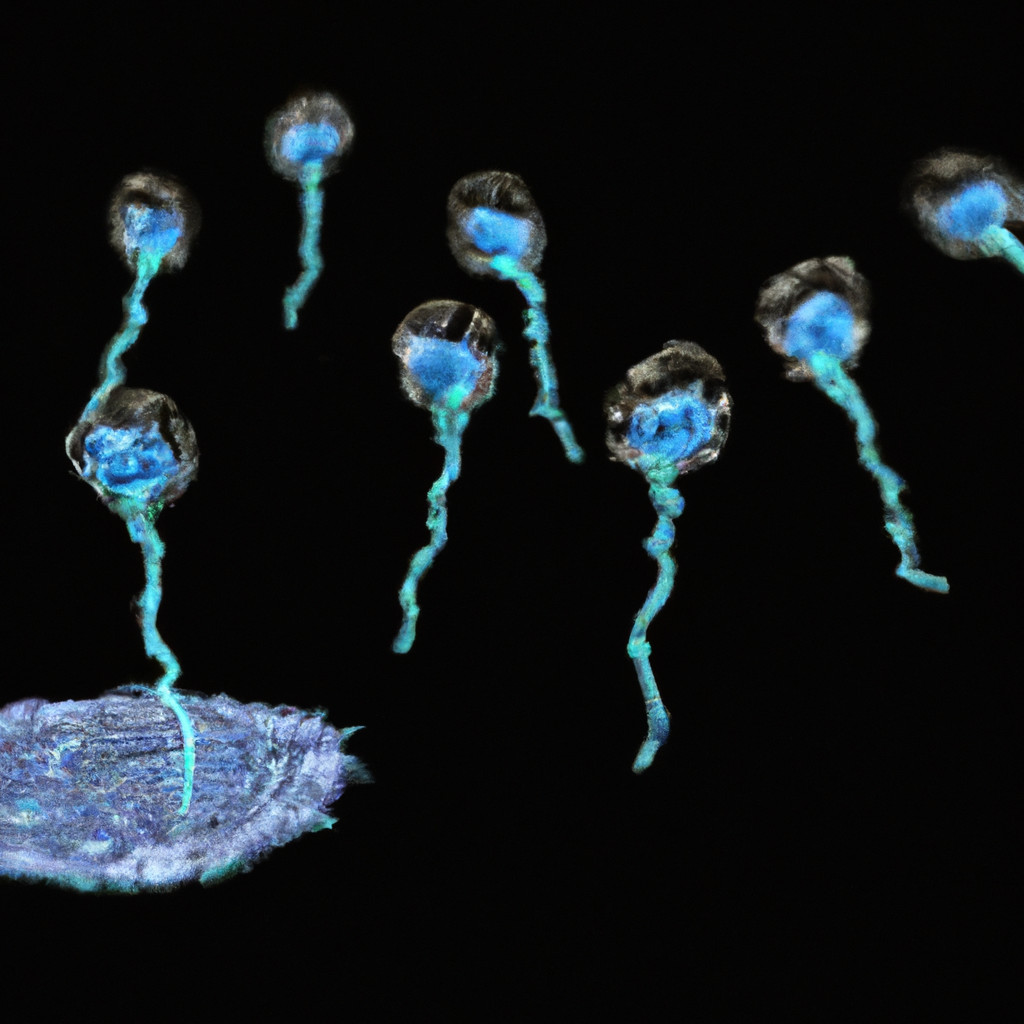
Islets are clusters of cells in the pancreas that produce insulin, a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels. In Type 1 Diabetes, the body’s immune system attacks these islets, leading to insulin deficiency. Accurate quantification of islets is crucial in understanding the progression of the disease and developing effective treatments.
Traditional methods of islet quantification are labor-intensive and prone to errors. However, the advent of deep learning has brought about a paradigm shift. Deep learning algorithms can analyze large volumes of data, identify patterns, and make predictions with high accuracy. In the context of islet quantification, these algorithms can analyze histological images, identify islets, and quantify them with remarkable precision.
The 77-PUB Study: A Game-Changer
The 77-PUB study is a landmark research that demonstrates the potential of deep learning in islet quantification. The study used a deep learning algorithm to analyze histological images from 77 publications. The algorithm was able to identify and quantify islets with an accuracy of 94%, significantly higher than traditional methods.
This study not only underscores the potential of deep learning in medical research but also paves the way for its application in the early detection and treatment of Type 1 Diabetes. By accurately quantifying islets, researchers can gain insights into the progression of the disease and develop personalized treatment plans.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite the promising results of the 77-PUB study, challenges remain in the implementation of deep learning in medical research. Data privacy is a major concern, as deep learning algorithms require large volumes of data. Ensuring the privacy and security of patient data is paramount.
Another challenge is the lack of transparency in deep learning algorithms. These algorithms are often referred to as “black boxes” because their decision-making processes are not easily understandable by humans. This lack of transparency can lead to mistrust and resistance among healthcare professionals.
Overcoming these challenges requires collaboration between the medical and tech industries. Further research is needed to improve the transparency of deep learning algorithms and to develop robust data privacy measures. With concerted efforts, the full potential of deep learning in healthcare can be realized.
FAQ Section
What is deep learning?
Deep learning is a subset of artificial intelligence that mimics the workings of the human brain in processing data and creating patterns for use in decision making.
What are islets?
Islets are clusters of cells in the pancreas that produce insulin, a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels.
How can deep learning help in islet quantification?
Deep learning algorithms can analyze histological images, identify islets, and quantify them with high accuracy, thereby improving the understanding of Type 1 Diabetes and aiding in its treatment.
What is the 77-PUB study?
The 77-PUB study is a research that used a deep learning algorithm to analyze histological images from 77 publications. The algorithm was able to identify and quantify islets with an accuracy of 94%.
What are the challenges in implementing deep learning in medical research?
Challenges include data privacy concerns and the lack of transparency in deep learning algorithms.
Conclusion: The Future of Deep Learning in Diabetes Research
The 77-PUB study has demonstrated the potential of deep learning in islet quantification, a crucial aspect of Type 1 Diabetes research. By accurately quantifying islets, deep learning can help in the early detection and treatment of the disease. However, challenges remain, including data privacy and algorithm transparency. Overcoming these challenges requires further research and collaboration between the medical and tech industries. With concerted efforts, the full potential of deep learning in healthcare can be realized.
[youtubomatic_search]
Further Analysis
As we delve deeper into the era of artificial intelligence, the intersection of deep learning and medical research continues to show promising results. The 77-PUB study is a testament to this, demonstrating the potential of deep learning in improving the understanding and treatment of Type 1 Diabetes. However, as with any technological advancement, challenges remain. Ensuring data privacy and improving algorithm transparency are paramount in the successful implementation of deep learning in healthcare. With further research and collaboration, these challenges can be overcome, paving the way for a new era in medical research and diagnosis.

Leave a Reply