-
Reading Roadmap
- Impact of UBE2E2 Overexpression on Glucose Intolerance in Mouse Pancreatic β-Cells
- Key Takeaways
- Introduction: Unraveling the Role of UBE2E2 in Glucose Metabolism
- UBE2E2 Overexpression and Glucose Intolerance
- UBE2E2 and Type 2 Diabetes
- UBE2E2 as a Potential Therapeutic Target
- FAQ Section
- What is UBE2E2?
- What is the impact of UBE2E2 overexpression on glucose intolerance?
- How is UBE2E2 associated with type 2 diabetes?
- Can UBE2E2 serve as a therapeutic target for diabetes treatment?
- What further research is needed on UBE2E2?
- Conclusion: The Potential of UBE2E2 in Diabetes Research and Treatment
- Further Analysis
Impact of UBE2E2 Overexpression on Glucose Intolerance in Mouse Pancreatic β-Cells
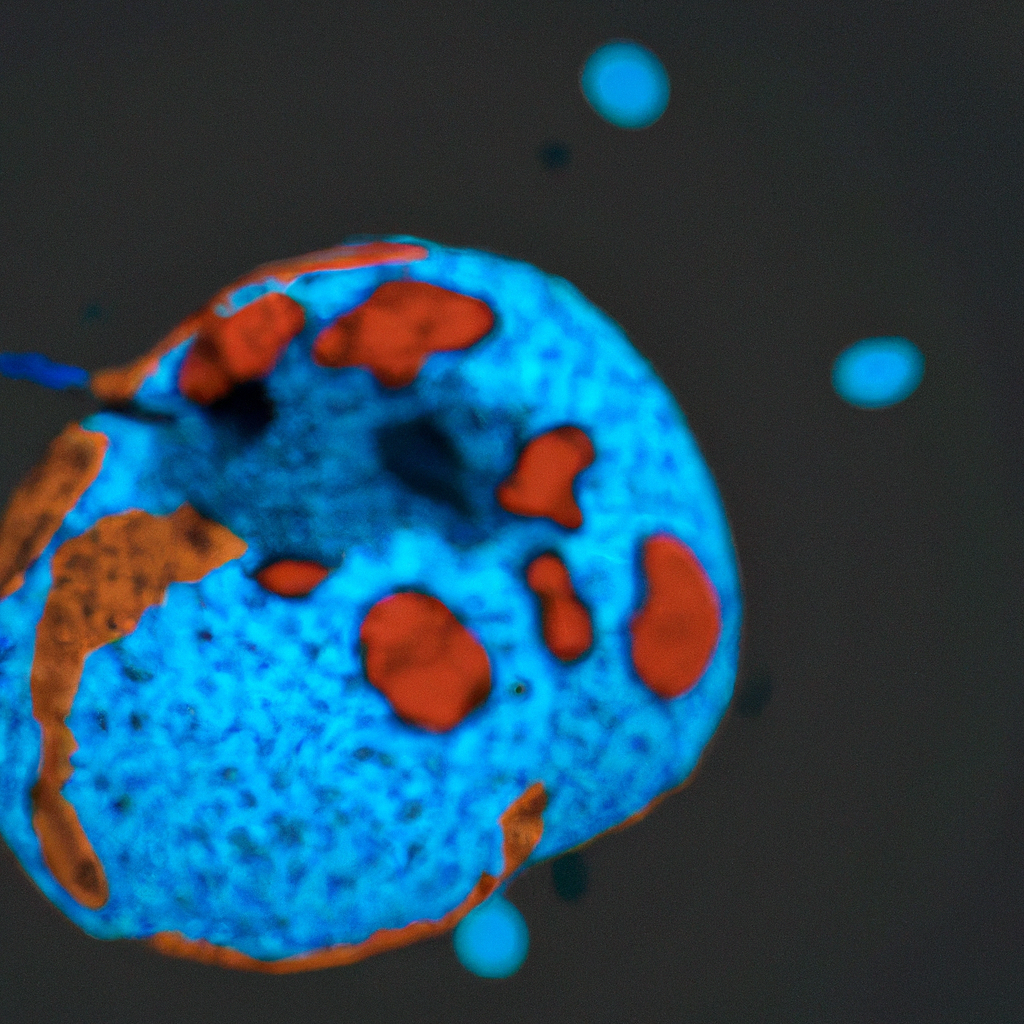
[youtubomatic_search]
Key Takeaways
- UBE2E2 overexpression in mouse pancreatic β-cells leads to glucose intolerance.
- UBE2E2 is a gene associated with type 2 diabetes in humans.
- Overexpression of UBE2E2 disrupts insulin secretion in β-cells.
- UBE2E2 overexpression could be a potential therapeutic target for type 2 diabetes.
- Further research is needed to fully understand the role of UBE2E2 in glucose metabolism.
Introduction: Unraveling the Role of UBE2E2 in Glucose Metabolism
UBE2E2, also known as ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 E2, is a gene that has been associated with type 2 diabetes in humans. Recent studies have shown that overexpression of this gene in mouse pancreatic β-cells leads to glucose intolerance, a precursor to diabetes. This article delves into the impact of UBE2E2 overexpression on glucose intolerance and its potential implications for diabetes research and treatment.
UBE2E2 Overexpression and Glucose Intolerance
Research has shown that overexpression of UBE2E2 in mouse pancreatic β-cells leads to glucose intolerance. This is due to the disruption of insulin secretion, a key process in glucose metabolism. Insulin is a hormone that allows cells to take in glucose from the bloodstream and use it for energy. When insulin secretion is disrupted, glucose levels in the blood can rise, leading to glucose intolerance and, eventually, diabetes.
UBE2E2 and Type 2 Diabetes
Studies have linked UBE2E2 to type 2 diabetes in humans. This form of diabetes is characterized by insulin resistance, where the body’s cells do not respond properly to insulin, and a lack of insulin production. Overexpression of UBE2E2 in β-cells could potentially contribute to both of these factors, making it a key area of interest for diabetes research.
UBE2E2 as a Potential Therapeutic Target
Given the impact of UBE2E2 overexpression on glucose intolerance and its association with type 2 diabetes, it could potentially serve as a therapeutic target for diabetes treatment. By targeting UBE2E2, it may be possible to restore normal insulin secretion and improve glucose tolerance. However, further research is needed to fully understand the role of UBE2E2 in glucose metabolism and its potential as a therapeutic target.
FAQ Section
What is UBE2E2?
UBE2E2, or ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 E2, is a gene that has been associated with type 2 diabetes in humans.
What is the impact of UBE2E2 overexpression on glucose intolerance?
Overexpression of UBE2E2 in mouse pancreatic β-cells leads to glucose intolerance due to the disruption of insulin secretion.
How is UBE2E2 associated with type 2 diabetes?
Studies have linked UBE2E2 to type 2 diabetes, a form of diabetes characterized by insulin resistance and a lack of insulin production.
Can UBE2E2 serve as a therapeutic target for diabetes treatment?
Given its impact on glucose intolerance and its association with type 2 diabetes, UBE2E2 could potentially serve as a therapeutic target for diabetes treatment. However, further research is needed.
What further research is needed on UBE2E2?
Further research is needed to fully understand the role of UBE2E2 in glucose metabolism and its potential as a therapeutic target.
Conclusion: The Potential of UBE2E2 in Diabetes Research and Treatment
The overexpression of UBE2E2 in mouse pancreatic β-cells and its impact on glucose intolerance provides valuable insights into the mechanisms of glucose metabolism and the development of type 2 diabetes. With its association with diabetes and its potential as a therapeutic target, UBE2E2 represents a promising area of research for diabetes treatment. However, further studies are needed to fully elucidate the role of UBE2E2 in glucose metabolism and its therapeutic potential.
[youtubomatic_search]
Further Analysis
As we delve deeper into the role of UBE2E2 in glucose metabolism, it is clear that this gene plays a significant role in the development of glucose intolerance and potentially type 2 diabetes. The overexpression of UBE2E2 disrupts insulin secretion in β-cells, leading to glucose intolerance. This disruption could potentially contribute to the development of type 2 diabetes, making UBE2E2 a key area of interest for diabetes research. With further research, UBE2E2 could potentially serve as a therapeutic target for diabetes treatment, offering new hope for those suffering from this chronic disease.

Leave a Reply